Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of more than 113 naturally occurring phytocannabinoids found in the hemp plant. Its recent rise in popularity has led to emerging scientific research confirming the multitude of therapeutic properties contained in what has historically been a controversial plant.
Many people have turned to CBD as a natural alternative to prescription medications and their harsh side effects.
The
Endocannabinoid
System
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is one of the most important physiologic systems involved in maintaining human health. Endocannabinoids and their receptors are found throughout the body. This system performs different tasks, but the main goal is to create a homeostatic environment. If the body suffers a lack of endocannabinoids, the result is Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency.
Dr. Ethan Russo is a neurologist well known for his extensive research on cannabis compounds and their role in the body. His study “Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects” details how the combination of all cannabinoids from the hemp plant work synergistically, creating an “Entourage Effect”, thus producing a greater therapeutic outcome. HEMP OneThirteen products are formulated with a multitude of phytocannabinoids, similar to the endocannabinoids found in the body.
CB1 Receptors
Primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, and to a lesser extent in other tissues.
Brain: CB1
Regulates: Neurological health (pain, anxiety, mood, sleep, focus, motor skills, short-term memory)
Lungs: CB1
Regulates: Respiratory health, asthma
Heart: CB1
Regulates: Inflammation, atherosclerosis
Immune System: CB2
Regulates: The body’s natural defense system
CB2 Receptors
Mostly located in the periphery, especially cells associated with the immune system.
Skin: CB2
Regulates: Dermatological inflammatory conditions (acne, scar, psoriasis, eczema)
Stomach: CB2
Regulates: Appetite, digestive support, gut health
Reproductive Organs: CB2
Regulates: Men’s and women’s health
Bones: CB2
Regulates: Bone strength, rheumatoid arthritis
How Does It Work
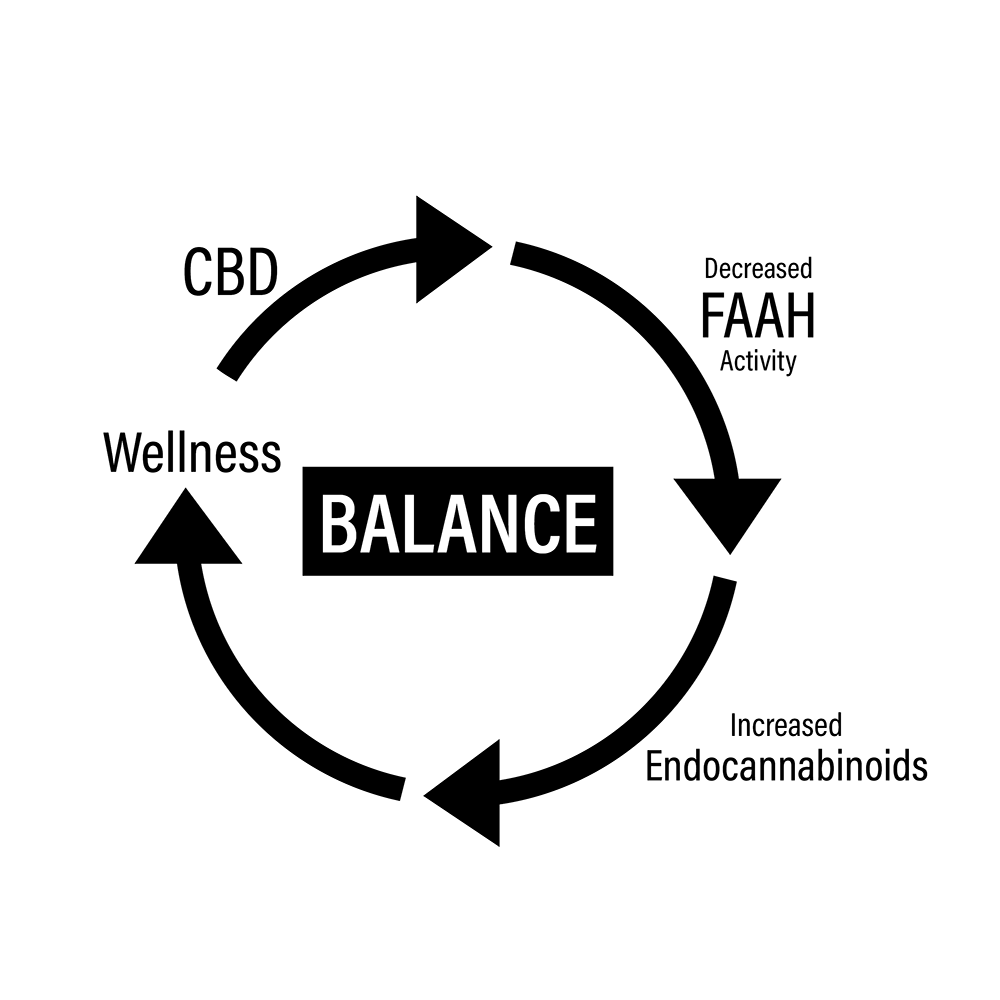
Anandamide A cannabinoid that occurs naturally in the body, Anandamide is responsible for activating the CB1 and CB2 receptors, which triggers the body’s natural protective response.
FAAH (fatty acid amide hydrolase) Breaks down Anandamide, limiting its ability to activate the CB1 and CB2 receptors.
CBD Supports natural endocannabinoid production and activity by slowing down Anandamide’s transport into the cell, thus decreasing breakdown by FAAH.





